

- #Macos malware years runonly to for pdf#
- #Macos malware years runonly to for code#
- #Macos malware years runonly to for download#
- #Macos malware years runonly to for mac#
YES if you are running untrusted applications or applications that may be exposed to malicious content (like Internet browsers, image previewers, PDF readers and so on). I have got an anti-virus/firewall software, do I need sandboxing then? This because by reducing the access level an application can have over your system you actually help the job of your anti-virus software.
Please note: Sandboxing does not eliminate the need for a good anti-virus system, it actually works in conjunction with your anti-virus software.
#Macos malware years runonly to for download#
Need to access external websites (and so, may download malicious content that may attempt to exploit your browser or its plugins)īy reducing access an application can have over your filesystem and resources helps to limit or even prevent (in some cases) the damages that an exploitation can do on your system.You don’t trust (for example applications you have downloaded from the internet that require you to allow their execution without being able to verify the source signature nor to check their source code).When should I use Application Sandboxing? the other is by running an arbitrary application using external sandboxing commands.
#Macos malware years runonly to for code#
#Macos malware years runonly to for mac#
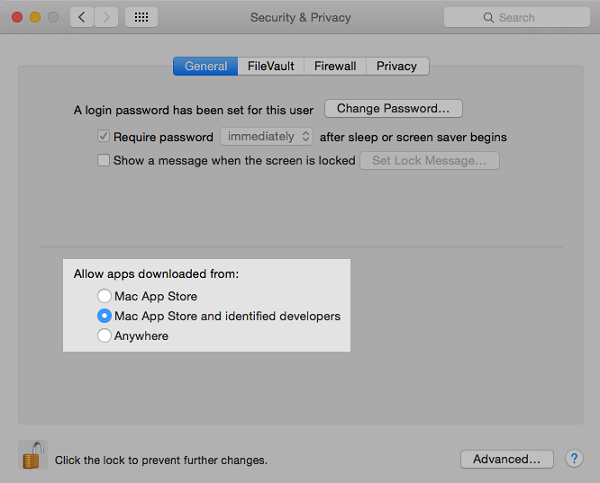
There are additional protections, particularly on a Mac with Apple silicon, to limit the potential damage of malware that does manage to execute. These protections, further described below, combine to support best-practice protection from viruses and malware. XProtect adds to this defense, along with Gatekeeper and Notarization.įinally, XProtect acts to remediate malware that has managed to successfully execute. The next layer of defense is to help ensure that if malware appears on any Mac, it’s quickly identified and blocked, both to halt spread and to remediate the Mac systems it’s already gained a foothold on. The first layer of defense is designed to inhibit the distribution of malware, and prevent it from launching even once-this is the goal of the App Store, and Gatekeeper combined with Notarization. Remediate malware that has executed: XProtect Block malware from running on customer systems: Gatekeeper, Notarization, and XProtectģ. Prevent launch or execution of malware: App Store, or Gatekeeper combined with NotarizationĢ. Malware defenses are structured in three layers:ġ. iPhone Text Message Forwarding security.How iMessage sends and receives messages.Adding transit and eMoney cards to Apple Wallet.Rendering cards unusable with Apple Pay.Adding credit or debit cards to Apple Pay.How Apple Pay keeps users’ purchases protected.Intro to app security for iOS and iPadOS.Protecting access to user’s health data.How Apple protects users’ personal data.Activating data connections securely in iOS and iPadOS.Protecting user data in the face of attack.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
